Application of ear endoscope in tympanic membrane repair
Surgical methods:
Use ear endoscope, with endoscope camera system, 24-inch high-definition medical monitor. Under local anesthesia, first take a piece of temporal muscle fascia from the temporal area and fix it with alcohol gauze for use. Observe the magnified video image of the external auditory canal, tympanic membrane, tympanum, and Eustachian tube opening through the monitor with ear endoscopes from various angles. If there is granulation in the tympanum, use microsurgery forceps to remove the granulation and suck the blood. Use adrenaline cotton pellets Press lightly to stop the bleeding, then observe whether the ossicle chain is complete, and use a microscopic probe to gently touch the ossicle to understand the activity of the ossicle, place a small stripper on the malleus, speak in a low voice, and ask the patient's hearing status, if the patient consciously Improved hearing indicates that the ossicular chain is complete and the activity is normal. Use a microscopic probe to scrape off the mucosal layer of about 2 to 3 mm (in smaller perforations) on the inner layer of the perforation edge of the tympanic membrane to prepare a transplant bed for the implantation method; you can also scrape the upper part of the same distance on the surface of the perforation edge of the tympanic membrane. The cortex may extend to the entire surface of the tympanic membrane to prepare a transplant bed for explantation. If it is a marginal perforation, first check whether there is epithelial ingrowth in the tympanic cavity. If there is epithelial ingrowth, use a cotton-wrapped probe to immerse in 50% trichloroacetic acid solution, and rub the ingrown epithelium under direct vision to remove it. Be careful not to touch the drum head. If there is no epithelial ingrowth, the transplant bed is expanded to the wall of the external auditory canal, and then the tympanum is filled with chloramphenicol oil gelatin sponge particles, and the pre-prepared fascia is taken out and flattened. According to the size of the perforation, it is trimmed to be 2~larger than the perforation. A suitable shape of 3mm is placed on the inner or surface of the tympanic membrane perforation. The graft is laid out according to the physiological angle, and then the surface of the transplant bed and the external auditory canal are filled with gelatin sponge. Anti-infective treatment is performed after 1 to 2 weeks in the ear endoscope Remove the external auditory canal packing carefully.
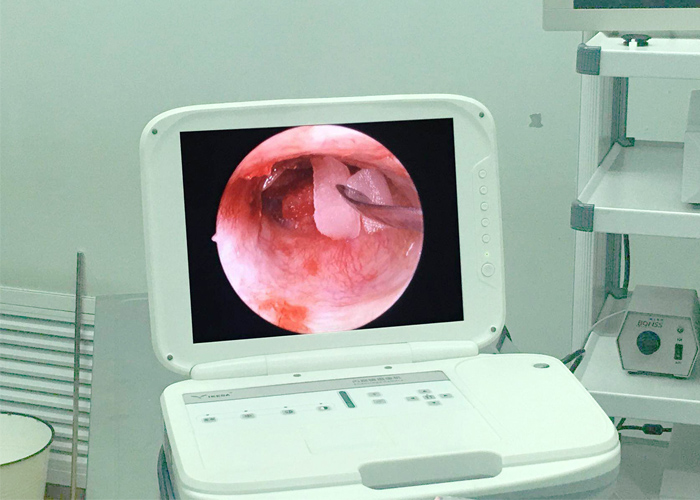
Comparison between ear endoscope and conventional surgery:
For tympanic membrane repair, the commonly used methods include cauterization and surgical repair, and the operation must be performed under a microscope. Its disadvantages are: ①The surgical instruments are large in size, inconvenient to move, and the operation is not flexible. They can only be used in limited spaces and cannot be moved between the operating room and the outpatient clinic for treatment and inspection; ②Because they are far away from the observed object, they are at a longer focal length. State, the viewing angle is very small, only part of the eardrum and tympanum can be observed through the external auditory canal, which is easy to leave dead corners. If you want to expand the observation range, you must cut the external auditory canal, and sometimes use an electric drill to sharpen the wall of the external auditory canal; ③Because of the specific focal length and Operate in a specific visual channel. When the patient or the surgeon moves, the observation channel and focus need to be re-adjusted to increase the operating procedures and prolong the operation time; ④ It is difficult for beginners to learn to use the microscope proficiently in a short period of time.
The tympanic membrane repair method under the ear endoscope is adopted. The advantages of this method are: ①Small size, convenient operation, and can be carried to different places at will; ②The focal length of the observation objective lens is short, the focal length is easy to adjust, the imaging is clear, the depth of field is wide, and the viewing angle is Large, can observe the panoramic view of the tympanic membrane and external auditory canal, and can observe the lesions in the tympanic cavity through the perforated tympanic membrane. It can be removed with microsurgery instruments under the endoscope. The operation is extremely simple. Use different angle endoscopic observations. The display is complete, and there is basically no dead space; ③The operation of placing the endoscope into the external auditory canal near the tympanic membrane can be performed under video images or under direct vision. It is not affected by changes in the position of the receptor, which greatly shortens the operation time; ④ No need to adjust the focus, easy to operate, easy for beginners to master. The shortcoming of the ear endoscope is that one hand-held ear endoscope and the other hand-held surgical instruments result in one-handed operation, which brings inconvenience to the operation. In addition, the ear endoscope needs to be placed in the external auditory canal, which also hinders the use of surgical instruments.